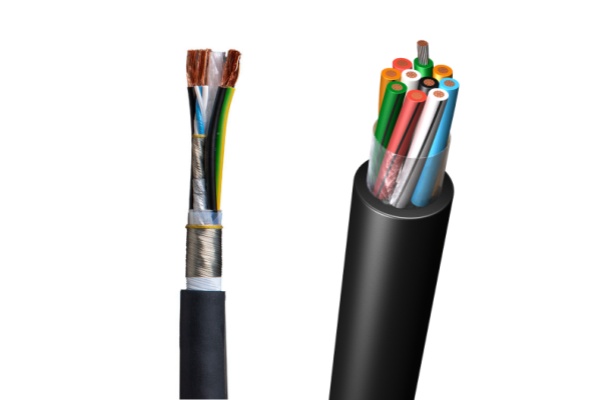
Control cables are essential components in industrial applications, facilitating communication, signal transmission, and control between machinery and automation systems. Without these cables, modern industries wouldn’t function efficiently or safely. These specialized cables are engineered to transmit electrical signals with minimal interference, ensuring precise operations across diverse environments, from factory floors to harsh outdoor settings.
In this article, VERI Cable will explore the common types of control cables used in industrial applications, focusing on their design, materials, and the specific environments where each type is most suitable. By understanding the different types, businesses can make informed decisions to optimize performance, reduce downtime, and enhance safety.
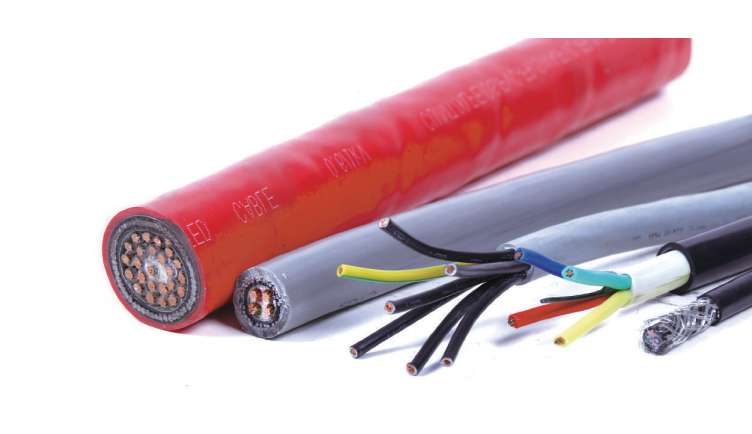

What are Control Cables?
Control cables are multi-conductor cables designed to carry low-voltage signals for the control and regulation of equipment. These cables are typically used in automation, manufacturing, energy, transportation, and other industries where precise control is essential.
They differ from power cables, which are meant to carry electrical current, in that they focus on signal integrity and minimal interference. The insulation and shielding of control cables are crucial to ensuring they transmit signals without degradation or electrical noise interference.
Now, let’s explore the various types of control cables commonly used in industrial applications:
1. PVC Control Cables
Overview:
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is one of the most widely used materials for control cables due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness. PVC control cables are typically used in industrial settings where moderate mechanical and chemical protection is required.
Key Characteristics:
- Flexibility: PVC cables offer a high degree of flexibility, making them ideal for installations requiring frequent bending or movement.
- Temperature Resistance: PVC control cables typically operate within a temperature range of -10°C to 70°C, making them suitable for indoor and controlled environments.
- Cost-Effective: These cables are relatively inexpensive and provide decent performance for various industrial tasks.
Common Applications:
- Automation systems
- Conveyor systems
- Packaging machinery
- Industrial robotics
PVC control cables are most effective in dry or mildly damp environments and can be used for light mechanical stress applications. While they are widely used, PVC cables have limited resistance to oils and chemicals, which may make them unsuitable for certain harsh environments.
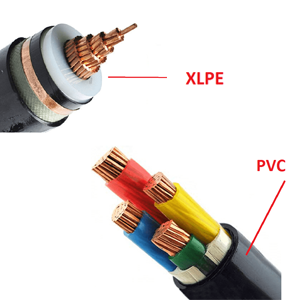
2. PUR Control Cables
Overview:
Polyurethane (PUR) control cables are known for their superior durability and resistance to abrasion, oils, and chemicals. PUR control cables are designed to withstand high mechanical stress and harsh environments, making them a popular choice for more demanding industrial applications.
Key Characteristics:
- High Durability: PUR cables are highly resistant to mechanical wear, making them suitable for environments where cables are exposed to abrasion, oils, and other chemicals.
- Temperature Range: These cables can operate in a wider temperature range than PVC cables, typically between -40°C to 90°C.
- Resistance to Environmental Factors: PUR control cables are highly resistant to oils, grease, and even ozone, making them ideal for use in chemically aggressive environments.
Common Applications:
- Machine tools
- Construction machinery
- Oil and gas industry
- Outdoor automation systems
These cables are preferred for applications where high mechanical stress is expected, such as dragging chains, mobile automation systems, and harsh industrial environments.
3. Shielded Control Cables
Overview:
Shielded control cables are designed to protect signal integrity in environments with high electromagnetic interference (EMI) or radio-frequency interference (RFI). These cables feature a shielding layer, typically made from materials like aluminum foil or copper braid, which helps reduce signal noise and interference.
Key Characteristics:
- Electromagnetic Protection: Shielded control cables are specifically engineered to maintain signal integrity by blocking interference from nearby electrical equipment.
- Various Shielding Options: These cables may use foil shielding, braid shielding, or a combination of both, depending on the level of protection required.
- Signal Accuracy: Shielded cables are essential for maintaining the accuracy of control signals in sensitive systems.
Common Applications:
- Industrial automation
- CNC machinery
- Robotics
- HVAC systems
In industries where sensitive control systems operate near power cables or heavy machinery, shielded control cables are essential to avoid signal degradation and ensure system reliability.
4. Instrumentation Control Cables
Instrumentation control cables are used where accurate and reliable signal transmission is critical for process control. These cables are specifically designed to handle low-voltage signals and are commonly used in industries where precision and data integrity are crucial, such as petrochemical, power generation, and pharmaceutical industries.
Key Characteristics:
- Signal Precision: These cables ensure the accurate transmission of low-voltage signals across long distances without signal degradation.
- Shielded Design: To minimize electromagnetic interference, instrumentation cables are often shielded.
- Multiple Pair Design: These cables typically come with multiple pairs of conductors, allowing for multiple signals to be transmitted simultaneously.
Common Applications:
- Power generation plants
- Petrochemical refineries
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Environmental monitoring systems
Instrumentation cables are critical for the smooth operation of control systems, particularly in industries with strict regulatory requirements and sensitive processes.
5. Flexible Control Cables
Flexible control cables are designed to maintain signal integrity even in dynamic applications, where constant motion or vibration occurs. These cables are used in industries where machinery is in constant motion, such as automation, robotics, and material handling systems.
Key Characteristics:
- High Flexibility: These cables are engineered with flexible materials, such as fine-stranded copper conductors and soft insulation, to endure frequent bending, twisting, and movement.
- Abrasion Resistance: The outer sheath of flexible control cables is often made from materials that can withstand mechanical wear and tear.
- Temperature and Environmental Resistance: These cables can operate in varying temperatures and are often resistant to oils and chemicals.
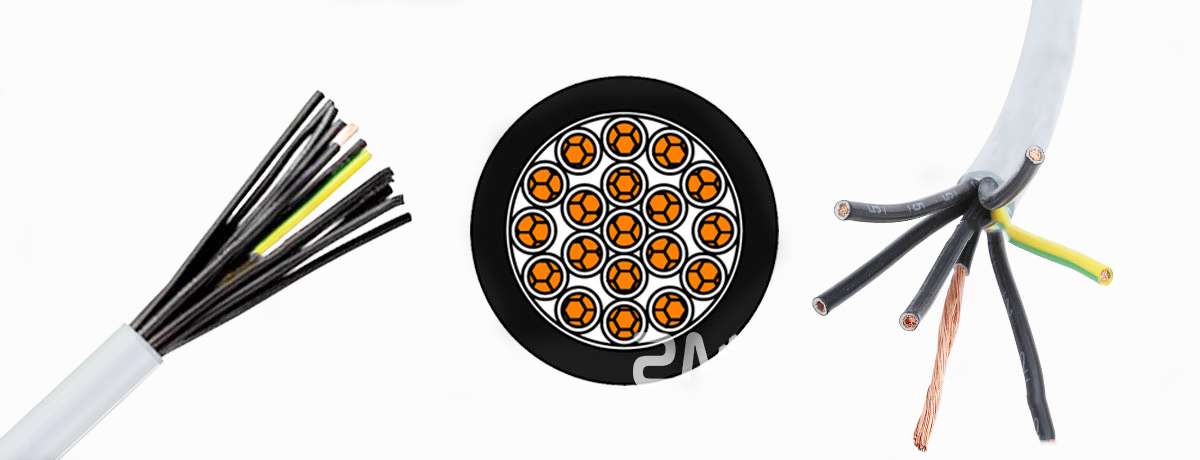

Common Applications:
- Conveyor systems
- Industrial robots
- Dynamic production lines
- Packaging and labeling machinery
The flexibility of these cables allows them to be used in machinery with moving parts without the risk of breakage or signal loss.
6. Halogen-Free Control Cables
Halogen-free control cables are designed to minimize the release of toxic gases in the event of a fire. These cables are made without halogens like chlorine, bromine, or fluorine, which can emit harmful gases when burned. Halogen-free cables are becoming increasingly important in industries with strict fire safety standards, such as transportation, data centers, and commercial buildings.
Key Characteristics:
- Fire Safety: Halogen-free cables are designed to emit low smoke and no halogen gases, making them safer in case of a fire.
- Environmental Benefits: These cables are environmentally friendly and compliant with many green building regulations.
- Durability: Despite being halogen-free, these cables offer robust mechanical protection and can endure moderate environmental stress.
Common Applications:
- Railway systems
- Data centers
- Commercial buildings
- Public infrastructure projects
In industries where fire safety is critical, halogen-free control cables help minimize the risk of toxic exposure during emergencies.
7. VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) Cables
Overview:
Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) cables are specialized control cables used to connect motors to variable frequency drives. These cables are designed to withstand the high levels of electrical noise and harsh conditions typically found in motor drive applications.
Key Characteristics:
- Noise Resistance: VFD cables are designed to handle the high levels of electrical noise generated by motor drives, ensuring signal integrity.
- Heat and Moisture Resistance: These cables are often built to withstand heat and moisture, as VFD systems can generate significant amounts of both during operation.
- Robust Construction: VFD cables are often shielded and built with reinforced insulation to handle the high power demands and harsh conditions in industrial settings.
Common Applications:
- Motor drives
- Conveyor belts
- HVAC systems
- Pumping stations
VFD cables ensure smooth and efficient motor operation, particularly in industrial applications requiring precise motor control.
8. Tray Cables
Tray cables are designed for installation in trays, conduits, and ducts in industrial settings. These cables are known for their durability, ease of installation, and ability to handle various electrical and mechanical stresses.
Key Characteristics:
- Versatile Installation: Tray cables can be installed in various ways, including open air, ducts, and conduits.
- High Resistance: These cables are resistant to oils, chemicals, and moisture, making them suitable for rugged environments.
- Multiple Conductors: Tray cables typically come with multiple conductors, allowing for the transmission of both power and control signals.
Common Applications:
- Power plants
- Chemical plants
- Wastewater treatment facilities
- Manufacturing plants
Tray cables are used extensively in industrial plants where complex control and power systems are required to operate machinery and automation systems.
9. Armored Control Cables
Armored control cables are designed for applications where high mechanical protection is necessary. These cables feature an additional layer of armor, typically made from steel wire or tape, which shields the cable from external damage.
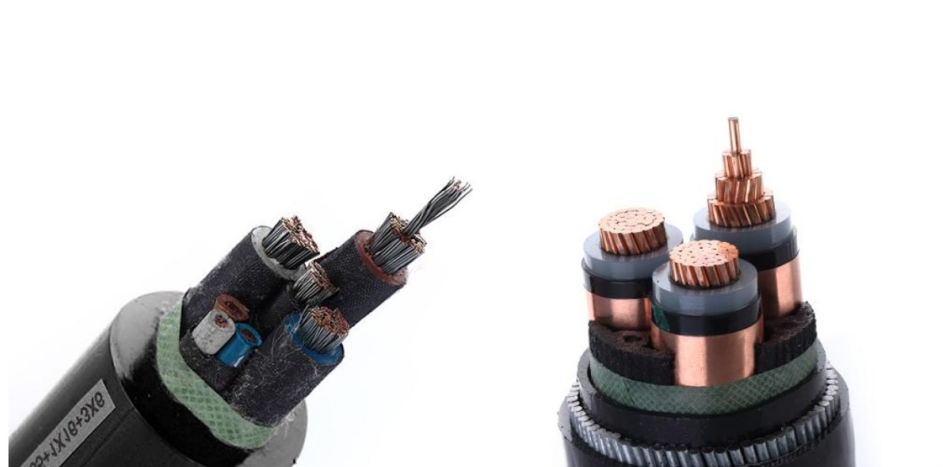

Key Characteristics:
- Enhanced Protection: The armored layer protects the cable from crushing, impact, and other forms of mechanical stress.
- Chemical Resistance: Armored control cables are often built with additional resistance to oils, chemicals, and moisture.
- Durability: These cables are designed to withstand harsh environments, both indoors and outdoors.
Common Applications:
- Mining
- Oil and gas
- Construction sites
- Heavy industrial applications
Armored control cables are essential for environments where cables are exposed to potential physical damage, ensuring continuous operation even under severe conditions.
Control cables are vital in the smooth operation of industrial systems. From PVC control cables used in basic automation to armored and VFD cables designed for the most extreme conditions, each type serves a specific role in optimizing industrial processes. Understanding the common types of control cables, their applications, and key characteristics can help industries select the right cables for their specific needs, improving safety, efficiency, and reliability across operations.
In today’s fast-paced industrial environments, choosing the right control cable is not just about performance; it is also about future-proofing against potential risks and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. With the right cable, industries can minimize downtime, reduce costs, and ensure the safety of both personnel and equipment.
