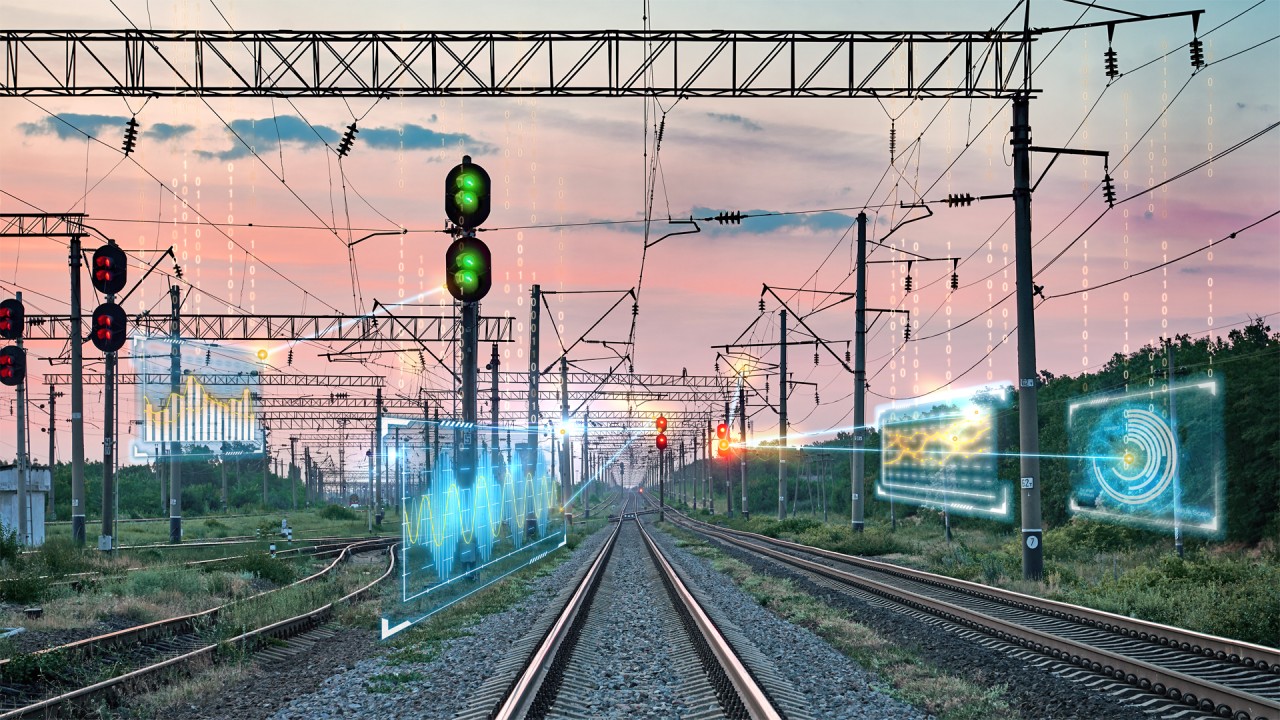

Overhead electric lines completed by the construction of overhead cables are one of the most common methods used in railroad electrification. Дегенмен, early reliance on battery-powered trains will become an essential option in some areas.
But for now, as global industrialization accelerates, annual carbon emissions continue to multiply, and the global warming trend becomes more pronounced, the most effective method of decarbonization is railroad electrification.
To achieve the best results of railroad electrification, people invented the overhead line with the third rail, today VERI cable is introduced to introduce the railroad electrification system in the overhead line mode of operation, interested in it, please continue to read it!


After electrification, the average cost is about 20% lower than the previous electric and diesel trains and the maintenance cost is 33% lower due to the lower manufacturing cost. This is one of the major focuses that has enabled the rapid growth of railroad trains after electrification.
Railroad electrification refers to railroads that can run electric trains, so named because of the need for electrification equipment along the lines of such railroads to provide power for the trains. Electrified railroads came into being with the emergence of electric locomotives, which do not carry their energy and require a constant flow of electricity from the power supply system along the railroad to drive the vehicles. Since electric locomotives have a stronger capacity advantage over internal combustion locomotives, the transport capacity of electrified railroads far exceeds that of non-electrified railroads on the same scale, and has become the mainstream type of modern railroads.
To cope with the safe and stable operation of trains in various situations, there are two mainstream methods of railroad electrification: one is the laying of overhead lines to deliver medium-voltage and high-voltage electricity, and the other is the laying of the third rail, which is the rail that can supply power to running trains.
Overhead lines, also known as overhead contact network systems, utilize a network of wires suspended above the track to supply power to trains. The system is mainly powered by alternating current (AC) and is widely used on mainline and high-speed rail networks.
When the overhead cables are connected to the electrified railroad power supply grid, they are divided into two categories: flexible and rigid, and electric locomotives or trainsets draw power from them by connecting them to the contact network via overhead pantographs.
In simple terms, such overhead and overhead cables supplying power to trains refer to commonly used high-voltage transmission lines.
Both conductor types, flexible and rigid, ultimately form circuits through the train’s normal running track ground. A few railroads also use a fourth rail (such as the famous London Underground) as a current loop.
One of the main advantages of overhead line electrification is its ability to transmit high-voltage power, typically 25 kV AC. This higher voltage enables efficient transmission over long distances, reduces energy losses, and lengthens the distance between power supply substations, thus reducing the number and cost of building power supply stations.
The famous Keiki Line in Japan took advantage of overhead high-voltage transmission as early as the twentieth century when the railroad’s operating track was improved.
Сондықтан, overhead electric lines are very suitable for railroads with decentralized power supply.
Another advantage of overhead lines for railroad electrification is that this high voltage is compatible with longer and heavier trains. High voltage power eliminates the need for on-board transformers, which reduces the weight and cost of rolling stock. In turn, this increases the capacity of the train, allowing for more passengers to be carried and improved operational efficiency.
When railroad electrification was not yet in common use, trains relying on battery-powered electricity had high annual carbon emissions, causing some pollution of the global air. In modern society, regardless of the use of high-voltage overhead line electrification or third rail, electric locomotives without exhaust, soot, no pollution to the air and other advantages are very suitable.
Сонымен қатар, the advantages of less noise, especially when passing through long tunnels, are even more significant. This not only improves the driver’s working conditions and passenger comfort but also minimizes noise pollution in cities and suburbs along the railroad.
Electric locomotives are equipped with high-power electric brakes for speed adjustment on long downhill gradients, which can significantly increase the safety of train operations.
In the many projects that VERI Cables has cooperated on, we have seen high-quality cables made by VERI for railroad systems arrive at the project site, be laid without problems, and the trains run smoothly, each project being a complete success. This is not possible without the construction of each worker in the development of modern society. Together, we make an outstanding contribution to the protection of the environment and the safe travel of mankind.
When people hear the term mineral insulated cable, many immediately think of harsh environments like…
As telecommunication networks and power transmission systems grow rapidly, the demand for reliable and cost-effective…
In large-scale oil and gas projects, industrial cables are not just accessories—they are the "nervous…
In the world of electrical connections, cable lugs—also known as cable ears or cable terminals—are…
When choosing the right rubber cable for an electrical engineering project, it is critical to…
Dear partners and customers: January 29th, 2025 is the Chinese Lunar New Year – Spring…