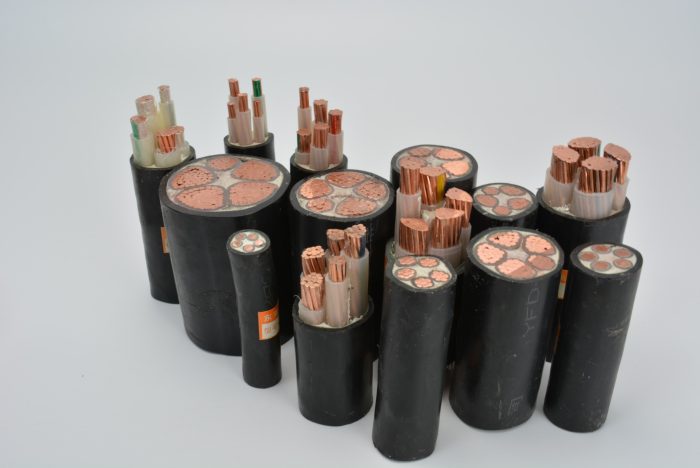

Жогорку чыңалуудагы кабелдер жер үстүндөгү жана жер астындагы төшөө ыкмаларында бар.
High voltage copper cables are essential components in the distribution and transmission of electrical power, offering both durability and excellent electrical conductivity. Understanding the structure, specifically the number of cores within these cables, is crucial to determining their functionality and applications in various industries. This article explores how many cores a high voltage copper cable normally has and delves into the typical applications of these cables across different sectors.


Before diving into the number of cores, it’s important to clarify what constitutes a high voltage copper cable. These cables are specifically designed to transmit electrical energy at high voltages, generally between 1 kV and 33 KV, though some high voltage cables can carry much higher voltages, particularly in transmission networks. The core of the cable is made from copper, known for its superior electrical conductivity compared to other materials, making it a popular choice in high-voltage systems.
The primary role of a high voltage copper cable is to ensure efficient power transmission while minimizing energy loss and maintaining safety. These cables are typically insulated with robust materials to withstand harsh environmental conditions and electrical stress.
One of the most common types of high voltage copper cables is the single-core cable. As the name suggests, a single-core cable contains only one conductor (core) surrounded by insulation and protective layers. These cables are widely used in various high-voltage applications, especially in large-scale power transmission systems.
Applications of Single-Core High Voltage Copper Cables:
In contrast to single-core cables, multi-core high voltage copper cables contain multiple conductors within a single outer sheath. The number of cores in these cables can vary, typically ranging from 2 чейин 4, although specific applications might require cables with more cores. Multi-core cables are often preferred in environments where space is limited, as they can transmit multiple electrical circuits simultaneously without the need for separate cables.
Two-core cables are less common in high voltage applications compared to single-core types. Бирок, they are sometimes used in specialized industrial settings where both power and communication signals need to be transmitted over the same cable.
Three-core high voltage copper cables are more prevalent in medium to high voltage applications. The three cores represent three-phase power transmission, which is essential for many industrial systems and large-scale energy distribution.
Applications of Three-Core High Voltage Copper Cables:
Four-core cables are generally used in low to medium voltage applications, though high voltage variants exist for specific needs. In high voltage scenarios, the fourth core may act as a neutral or as an earth conductor, depending on the system’s configuration.
Applications of Four-Core High Voltage Copper Cables:
Several factors influence the number of cores chosen for a high voltage copper cable:
High voltage copper cables are widely used for transmitting electricity from power generation stations to substations and ultimately to end users. They play a vital role in ensuring the efficient transfer of large amounts of electricity over long distances, minimizing energy loss.
In large industrial complexes, high voltage copper cables are used to supply power to heavy machinery, Мотор, and other equipment that require substantial electrical loads. The robust design and high conductivity of copper ensure that these systems run smoothly without interruptions.
Renewable energy systems, such as wind farms and solar power plants, rely on high voltage copper cables to connect generation units to the main power grid. These cables are essential in transporting clean energy over long distances, ensuring it reaches the grid with minimal losses.
High voltage copper cables are often installed underground or underwater to transmit electricity in environments where overhead cables are impractical. These cables must be durable enough to withstand harsh conditions, including moisture, pressure, and temperature fluctuations.
The transportation industry, especially railways, also uses high voltage copper cables for signaling, control systems, and electrified train lines. These cables provide power for the smooth operation of electric trains, trams, and other high-speed rail systems.
In telecommunications, high voltage copper cables are used in conjunction with other transmission media to power base stations, data centers, and other communication infrastructure. Copper’s excellent conductivity and reliability make it an ideal choice for these critical systems.
High voltage copper cables come in various core configurations, depending on the specific application and the electrical system requirements. Single-core, two-core, three-core, and four-core copper cables all have their uses in different sectors, ranging from power transmission and industrial applications to renewable energy and telecommunications. Their versatility, combined with copper’s superior conductivity, durability, and reliability, ensures that high voltage copper cables remain a fundamental component in modern electrical infrastructure.
Whether used in large power grids, industrial complexes, or renewable energy projects, these cables play a crucial role in ensuring the efficient and safe transmission of electrical energy across the globe. Understanding the different configurations and applications helps engineers and electricians choose the right type of cable for their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
When people hear the term mineral insulated cable, many immediately think of harsh environments like…
As telecommunication networks and power transmission systems grow rapidly, the demand for reliable and cost-effective…
In large-scale oil and gas projects, industrial cables are not just accessories—they are the "nervous…
In the world of electrical connections, cable lugs—also known as cable ears or cable terminals—are…
When choosing the right rubber cable for an electrical engineering project, it is critical to…
Урматтуу өнөктөштөр жана кардарлар: 29-январь, 2025 Кытайдын Ай Жаңы жылы – Spring…