Thermocouple cables are essential components in industrial temperature measurement systems. These cables are used to connect thermocouples, which measure temperature by generating a voltage proportional to the temperature difference between two dissimilar metal junctions. The correct selection of thermocouple cable is critical for ensuring accurate temperature readings, making it vital to understand its classifications and applications.
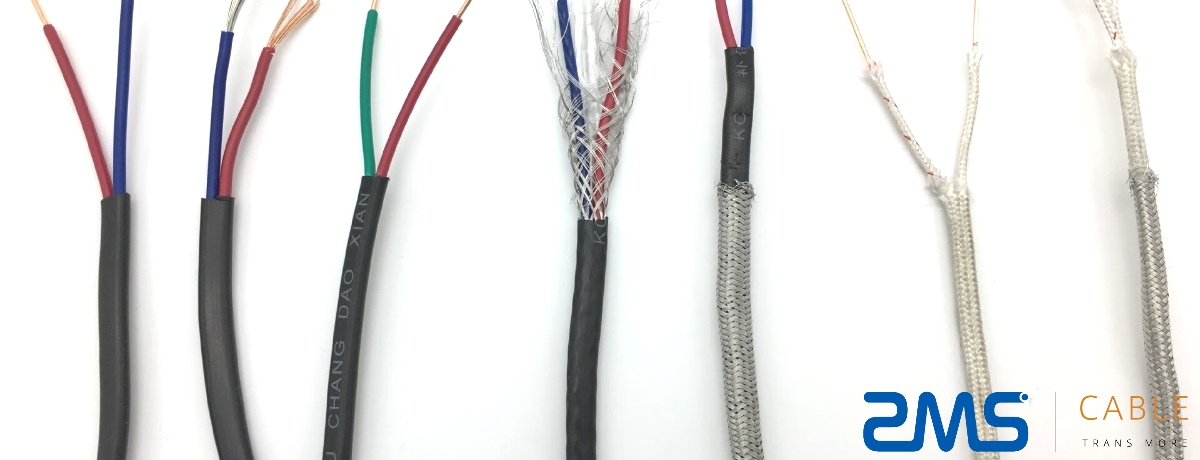

This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about thermocouple cables, from their classifications to the various industries and applications that rely on them.
What is a Thermocouple Cable?
A thermocouple cable is a specialized wire used to connect a thermocouple sensor to a measuring instrument, such as a temperature controller, meter, or data logger. The cable maintains the integrity of the thermocouple system by ensuring that the temperature signal is not altered or lost during transmission from the sensor to the instrument.
Thermocouple cables are constructed with specific metals or alloys to match the thermocouple type, ensuring that the thermal response characteristics remain accurate throughout the measurement process. These cables are also designed to withstand harsh industrial environments, w tym ekstremalne temperatury, chemicals, and mechanical wear.
Components of a Thermocouple Cable
A typical thermocouple cable consists of:
- Conductor wires: Made from specific alloys corresponding to the thermocouple type.
- Izolacja: Prevents electrical interference and maintains the physical integrity of the cable.
- Outer jacket: Provides additional protection against environmental factors, such as chemicals, wilgoć, and abrasion.
Classifications of Thermocouple Cables
Thermocouple cables are classified based on various factors, including thermocouple types, insulation materials, temperature range, and application environment.
Below are some of the key classifications:
1. Thermocouple Type
Thermocouple cables are classified by the thermocouple types they support.
The most common types are as follows:
Type K (Nickel-Chromium / Nickel-Aluminum): One of the most widely used thermocouples due to its wide temperature range (-200°C to 1350°C) and general reliability. Suitable for oxidizing environments.
Type J (Iron / Constantan): Offers a more limited temperature range (-40°C to 750°C) compared to Type K, but it is ideal for reducing atmospheres.
Type T (Copper / Constantan): Operates at low temperatures (-250°C to 400°C) and is known for its high accuracy in cryogenic applications.
Type E (Nickel-Chromium / Constantan): Provides a high output for small temperature changes, useful for a temperature range of -270°C to 1000°C.
Type N (Nickel-Chromium-Silicon / Nickel-Silicon-Magnesium): A stable thermocouple for use at high temperatures (up to 1300°C), with better resistance to oxidation and drift compared to Type K.
Type S, R, and B (Platinum-Rhodium Alloy): These platinum-based thermocouples are suitable for extremely high-temperature applications, especially in laboratories and industries requiring temperature measurements above 1450°C.
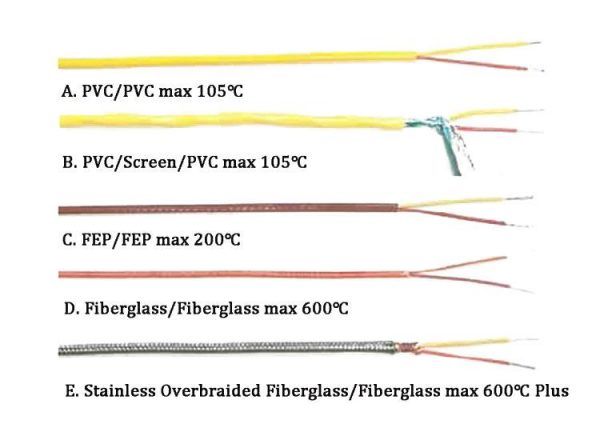
2. Materiał izolacyjny
The insulation material is crucial in determining where a thermocouple cable can be used. Here are common types of insulation materials and their benefits:
PCV (Polyvinyl Chloride): Provides resistance to moisture and chemicals. Suitable for general-purpose and low-temperature applications up to 105°C.
Teflon (PTFE): Offers excellent resistance to chemicals, wilgoć, and high temperatures (up to 260°C). Ideal for high-temperature and corrosive environments.
Fiberglass: Resistant to high temperatures (up to 480°C) but less effective in moisture-laden environments. Commonly used in industrial settings with extreme heat.
Silicone Rubber: Known for its flexibility and resistance to both high temperatures and chemicals, making it perfect for dynamic environments.
Ceramic Fiber: Can withstand temperatures as high as 1200°C. Used in specialized high-temperature applications, especially when flame resistance is critical.
3. Temperature Range
Thermocouple cables are selected based on their temperature tolerance, which corresponds to the material of the conductor and the insulation. Type K, for example, has a broad temperature range, making it versatile for various industries.
4. Shielding and Armoring
In some environments, thermocouple cables may require additional protection from external factors like electromagnetic interference (EMI), mechanical damage, and moisture. Common shielding and armoring techniques include:
Metal Braids or Foil Shields: To protect against electromagnetic interference and maintain signal integrity.
Armor Jackets: A robust protective layer made from stainless steel or aluminum to guard against physical damage.
Applications of Thermocouple Cables
Thermocouple cables are used across numerous industries due to their versatility, trwałość, and accuracy in temperature measurement. Below are some of the most common applications:
1. Industrial Manufacturing
Maintaining precise temperature control is vital in industries such as steel, cement, glass, and plastics manufacturing. Thermocouples and their accompanying cables monitor and regulate high-temperature processes, ensuring quality control and safety in production.
- Furnaces: Thermocouples help in monitoring furnace temperatures, which often exceed 1000°C in steel manufacturing.
- Injection Molding: Used in plastics manufacturing to monitor mold and barrel temperatures.
- Kilns: Used in the ceramics and cement industries for accurate control of kiln temperatures.
2. Oil and Gas
In the oil and gas sector, thermocouple cables are deployed in harsh environments, such as offshore platforms, refineries, and petrochemical plants. They are used to monitor the temperature of pipelines, drilling equipment, and other systems that operate in extreme conditions.
- Refineries: Thermocouples measure temperature in distillation columns, catalytic crackers, and heat exchangers.
- Exploration: Thermocouple cables are used in high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) environments to monitor wellhead and downhole temperatures.
3. Power Generation
Thermocouple cables are extensively used in power generation plants, especially in turbines, boilers, and reactors, where temperature management is essential for efficiency and safety.
- Steam Turbines: Thermocouples help monitor and control the temperature of steam to optimize power output and efficiency.
- Nuclear Reactors: Thermocouples provide critical temperature readings to maintain reactor stability and prevent overheating.
4. Aerospace and Defense
The aerospace industry demands precise and reliable temperature measurement during extreme conditions during manufacturing and flight operations.
Thermocouples are often used in:
- Jet Engines: Monitoring exhaust gas temperatures (EGT) and turbine inlet temperatures (TIT) is critical for engine performance.
- Spacecraft: Thermocouples play a crucial role in monitoring temperatures during launch, re-entry, and other phases of space missions.

5. HVAC Systems
Thermocouple cables are commonly used in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems to monitor temperature and ensure energy efficiency. They are utilized in thermostats, heat pumps, and refrigeration systems for precise temperature control.
6. Food and Beverage
Maintaining proper temperature in the food industry is essential for safety and quality control. Thermocouple cables are used to monitor cooking, cooling, and storage temperatures, ensuring compliance with health and safety regulations.
- Ovens and Grills: Monitoring the internal temperature of cooking appliances helps maintain consistent cooking quality.
- Cold Storage: Used to track the temperature of refrigerated goods to prevent spoilage.
7. Medical Devices
In medical applications, thermocouples are essential for monitoring patient body temperatures during surgical procedures and in critical care environments. They are also used in sterilization processes for medical equipment, ensuring safe and effective results.
Benefits of Using Thermocouple Cables
Thermocouple cables offer several benefits, making them indispensable in temperature measurement systems:
- Accuracy: Thermocouple cables ensure precise transmission of temperature signals, helping maintain accuracy in readings.
- Trwałość: These cables are designed to withstand harsh environments, including high temperatures, corrosive conditions, and physical wear.
- Versatility: With different thermocouple types and insulation materials, these cables are adaptable to a wide range of applications.
- Cost-Effective: Thermocouple systems are generally more affordable compared to other temperature measurement technologies, such as resistance temperature detectors (RTDs).
Selection Criteria for Thermocouple Cables
When selecting the right thermocouple cable for your application, consider the following factors:
- Temperature Range: Choose a cable that can withstand the temperatures in your specific environment.
- Materiał izolacyjny: Select the appropriate insulation for the conditions (e.g., chemical exposure, wilgoć, abrasion).
- Accuracy Requirements: Ensure that the thermocouple type and cable material match your accuracy and sensitivity needs.
- Environmental Conditions: Determine whether shielding or armoring is required to protect the cable from EMI, mechanical damage, or harsh weather conditions.
- Cost: Consider the long-term durability and efficiency when factoring in cost.
Thermocouple cables play a vital role in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of temperature measurement systems across various industries. Understanding their classifications, applications, and benefits can help you select the right cable for your specific needs, ensuring optimal performance in even the most challenging environments. Whether you’re working in manufacturing, aerospace, oil and gas, or the food industry, thermocouple cables provide the precision and durability required for critical temperature monitoring tasks.
By choosing the right thermocouple cable, businesses can improve safety, efficiency, and product quality, all while ensuring long-term reliability and cost-effectiveness.