Instrumentation cables are critical components in industrial and commercial settings, used to transmit data and signals for monitoring and controlling equipment. They are designed to maintain signal integrity in environments that may present electrical noise, mechanical stress, and environmental hazards. These cables are vital in precise control and measurement processes, such as in chemical plants, power generation, oil and gas industries, and automation systems. This essay VERI cable explores the various types of instrumentation cables, their specific models, and their applications, highlighting their importance in modern technological landscapes.
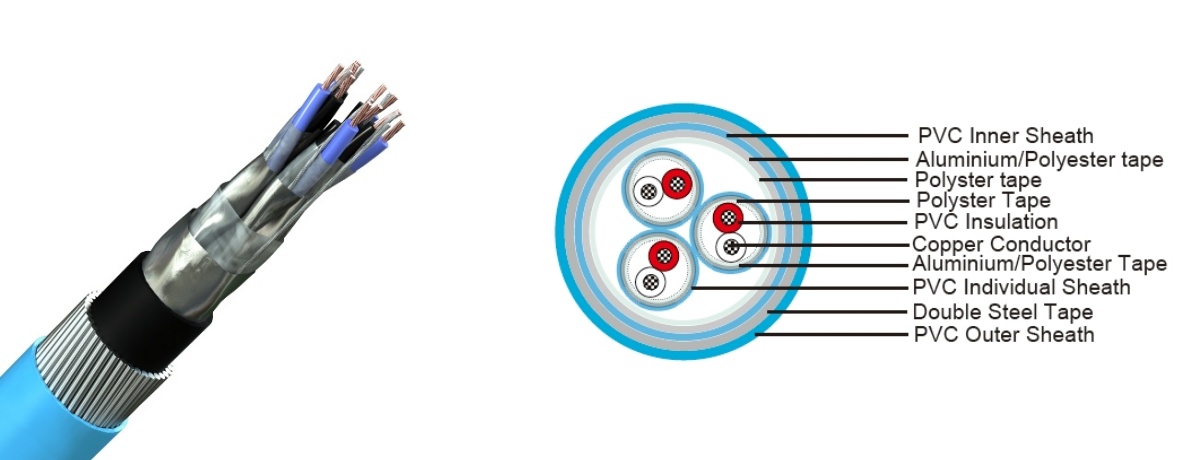
Noocyada Xargaha Qalabka
Instrumentation cables come in various configurations, each designed to meet specific requirements. The primary types include:
- Paired Cables
- Triad Cables
- Multi-pair Cables
- Shielded and Unshielded Cables
- Thermocouple Extension Cables
- Fieldbus Cables
Paired Cables
Paired cables consist of two insulated conductors twisted together. This configuration helps minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk between adjacent pairs. The twisting of the pairs is essential in maintaining signal integrity over long distances.
Codsiyada:
- Data Transmission: Used in systems requiring low-frequency data transmission.
- Audio Equipment: Commonly found in professional audio systems for balanced audio signals.
- Industrial Control Systems: Utilized in environments where noise reduction is critical for accurate signal transmission.
Triad Cables
Triad cables consist of three insulated conductors twisted together. The triad configuration is particularly useful in applications requiring multiple signal paths within a single cable, reducing the need for multiple cable runs.
Codsiyada:
- Process Control: Often used in analog and digital signal transmission for process control systems.
- Instrumentation Systems: Suitable for complex instrumentation systems requiring multiple signal transmissions.
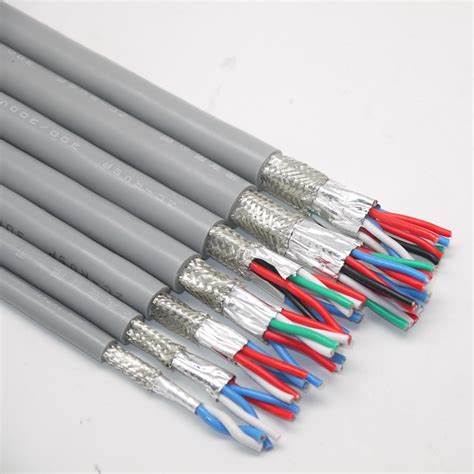

Multi-pair Cables
Multi-pair cables consist of several pairs of twisted conductors, allowing multiple signals to be transmitted through a single cable. These cables are particularly advantageous in reducing the physical space required for wiring and simplifying installation.
Codsiyada:
- Telecommunications: Extensively used in telephone systems and data networks.
- Control Systems: Employed in industrial control systems to transmit multiple signals from various sensors and controllers.
Shielded and Unshielded Cables
Instrumentation cables can be either shielded or unshielded. Shielded cables incorporate a conductive material layer around the conductors to protect against EMI. Unshielded cables, as the name suggests, do not have this layer.
Shielded Cables Applications:
- High-EMI Environments: Used in environments with significant electromagnetic interference to ensure signal integrity.
- Sensitive Equipment: Ideal for connecting sensitive electronic equipment that can be affected by external noise.
Unshielded Cables Applications:
- Low-EMI Environments: Suitable for use in areas with minimal electromagnetic interference.
- Short Distance Communication: Used where cable runs are short and EMI is not a significant concern.
Thermocouple Extension Cables
Thermocouple extension cables are specifically designed for connecting thermocouples to measuring instruments. These cables must be made from materials compatible with the thermocouple to ensure accurate temperature readings.
Codsiyada:
- Temperature Measurement: Extensively used in industrial settings for precise temperature monitoring and control.
- Process Control: Critical in processes where temperature control is essential for safety and quality.
Fieldbus Cables
Fieldbus cables are used in digital, two-way communication systems for industrial automation. These cables enable multiple field devices to be connected on a single network.
Codsiyada:
- Automation Systems: Integral to industrial automation systems, providing reliable and efficient communication between devices.
- Process Industries: Used in process industries such as oil and gas, kiimiko, and pharmaceutical for robust data transmission.

Instrumentation Cable Models
Different models of instrumentation cables are designed to meet specific standards and applications. These models include:
- PLTC (Power Limited Tray Cable)
- TC (Tray Cable)
- PLTC-ER (Power Limited Tray Cable-Exposed Run)
- Type ITC (Instrumentation Tray Cable)
PLTC (Power Limited Tray Cable)
PLTC cables are designed for installation in cable trays and other industrial environments. They are suitable for power-limited circuits and comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC) requirements.
Codsiyada:
- Control Circuits: Used in control circuits where the voltage does not exceed 300 volts.
- Communication Systems: Suitable for communication and signaling systems in industrial environments.
TC (Tray Cable)
Tray cables (TC) are versatile cables designed for installation in trays, conduits, and other raceways. They are suitable for a wide range of industrial applications and comply with NEC requirements for tray cables.
Codsiyada:
- Power Distribution: Used for power distribution in industrial settings.
- Control and Signal Circuits: Ideal for control and signal circuits requiring robust cable construction.
PLTC-ER (Power Limited Tray Cable-Exposed Run)
PLTC-ER cables are similar to PLTC cables but are rated for exposed runs, meaning they can be installed outside of conduit or cable trays for limited distances. This makes installation more flexible and cost-effective.
Codsiyada:
- Exposed Runs: Suitable for applications where cables need to run exposed for short distances.
- Industrial Control Systems: Used in industrial control systems where installation flexibility is required.
Type ITC (Instrumentation Tray Cable)
Type ITC cables are designed specifically for instrumentation and control applications. They offer superior protection against EMI and are suitable for installation in trays, conduits, and raceways.
Codsiyada:
- Instrumentation Systems: Used extensively in instrumentation systems for reliable signal transmission.
- Process Control: Ideal for process control applications requiring high levels of signal integrity.
Applications of Instrumentation Cables
Instrumentation cables are indispensable in various industries, ensuring accurate data transmission and control. Some key applications include:
Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas industry, instrumentation cables are critical for monitoring and controlling various processes. They are used in:
- Drilling Operations: To transmit data from sensors monitoring pressure, temperature, and flow rates.
- Refineries: For process control and monitoring in refineries, ensuring safe and efficient operations.
- Pipeline Monitoring: To monitor the integrity and flow of pipelines, detecting leaks or anomalies in real time.
Power Generation
Power generation facilities rely heavily on instrumentation cables for monitoring and control. Applications include:
- Turbine Control: Used to transmit data from sensors monitoring turbine performance.
- Environmental Monitoring: For monitoring emissions and environmental conditions in power plants.
- Safety Systems: Integral to safety systems that ensure the safe operation of power generation equipment.

Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industries
In chemical and pharmaceutical industries, precision and reliability are paramount. Instrumentation cables are used in:
- Process Control: To monitor and control chemical reactions and processes.
- Quality Control: Ensuring accurate data transmission for quality control systems.
- Environmental Monitoring: Monitoring environmental conditions to maintain safety and compliance with regulations.
Automation and Control Systems
Automation and control systems across various industries depend on instrumentation cables for reliable data transmission.
Applications include:
- Factory Automation: Used in automated production lines for control and monitoring of machinery.
- Building Management Systems: For monitoring and controlling HVAC, lighting, and security systems.
- Robotics: Integral to robotic systems requiring precise control and data transmission.
Telecommunications
In telecommunications, instrumentation cables are essential for reliable data transmission. Applications include:
- Data Centers: Used in data centers for high-speed data transmission and network management.
- Communication Networks: For transmitting signals in communication networks, ensuring reliable connectivity.
- Broadcasting: Used in broadcasting systems for transmitting audio and video signals with high fidelity.
Instrumentation cables play a crucial role in modern industrial and commercial applications, ensuring accurate and reliable data transmission and control. The various types and models of instrumentation cables are designed to meet specific requirements, providing solutions for environments with high electromagnetic interference, mechanical stress, and environmental hazards. From oil and gas industries to power generation, chemical manufacturing, automation systems, and telecommunications, instrumentation cables are indispensable in maintaining the integrity and efficiency of critical processes. Understanding the different types of instrumentation cables and their applications helps in selecting the right cable for each specific need, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.