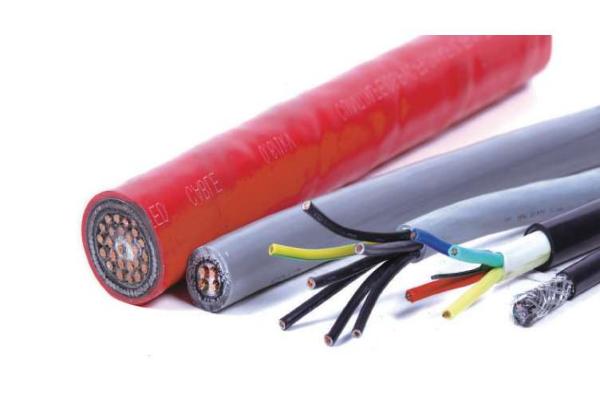

Outdoor cables play a pivotal role in modern infrastructure, facilitating communication, power distribution, and data transmission across vast distances. Whether it’s for telecommunication networks, power grids, or outdoor installations, the right external cables can make all the difference in reliability, efficiency, and longevity. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the various types and models of outdoor cables available, their applications, and considerations for selecting the most suitable option for specific needs.
Fiber optic cables are renowned for their high-speed data transmission capabilities and immunity to electromagnetic interference. They consist of one or more optical fibers enclosed in protective layers. Outdoor fiber optic cables are designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures, moisture, and UV exposure. They are commonly used in long-distance telecommunications networks, internet infrastructure, and outdoor surveillance systems.


Model: Loose Tube Fiber Optic Cable
Примена: Long-distance telecommunications networks, internet backbone infrastructure, outdoor surveillance systems, and data centers requiring high-speed data transmission over extended distances.
Coaxial cables feature a central conductor, surrounded by a dielectric insulator, a conductive shield, and an outer insulating layer. They are widely used for transmitting high-frequency signals with minimal interference. Outdoor coaxial cables are commonly employed in cable television distribution networks, satellite communications, and broadband internet connections.
Model: RG-6 Coaxial Cable
Примена: Cable television distribution networks, satellite communications, broadband internet connections, and outdoor CCTV systems requiring reliable signal transmission with minimal interference.
Twisted pair cables consist of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference. They are versatile and cost-effective, making them suitable for various outdoor applications. Outdoor twisted pair cables are commonly used in telephone networks, Ethernet connections, and outdoor surveillance systems.
Model: Cat 6 Outdoor Ethernet Cable
Примена: Outdoor Ethernet connections, telephone networks, surveillance systems, and outdoor access points requiring high-speed data transmission over short to moderate distances.
Direct burial cables are specifically designed for underground installations without the need for conduit or ducts. They feature robust insulation and protective layers to withstand moisture, soil pressure, and other environmental factors. Direct burial cables are commonly used for outdoor lighting, underground power distribution, and irrigation systems.
Model: UF-B Underground Feeder Cable
Примена: Underground power distribution, lighting, irrigation systems, and landscape lighting requiring durable cables capable of withstanding direct burial without conduit.
Armored cables feature an additional layer of metal armor for enhanced mechanical protection. They are highly durable and resistant to physical damage, making them ideal for outdoor installations in challenging environments. Armored cables are commonly used in industrial applications, outdoor power distribution, and marine installations.
Model: SWA Armored Power Cable
Примена: Industrial installations, outdoor power distribution, marine environments, and areas prone to mechanical damage requiring robust cables with enhanced protection against physical hazards.
Consider the specific environmental conditions where the cable will be installed, including temperature fluctuations, moisture levels, UV exposure, and potential exposure to chemicals or abrasive materials.
Determine whether the cable will be installed above ground, подземни, or underwater, and consider factors such as burial depth, conduit availability, and the need for additional protection against physical damage.
Evaluate the required data transmission speeds, signal integrity, and electrical characteristics to ensure that the selected cable meets the performance requirements of the application.
Choose cables with robust construction and protective layers to ensure long-term durability and reliability, particularly in harsh outdoor environments prone to extreme weather conditions or physical hazards.
Ensure that the selected cable complies with relevant industry standards and certifications to guarantee quality, safety, and compatibility with existing infrastructure and equipment.
Outdoor cables and indoor cables serve different purposes and are designed to withstand different environmental conditions. The main differences between outdoor and indoor cables are as follows:
Outdoor cables are constructed with materials and designs that provide resistance to harsh outdoor conditions such as moisture, UV exposure, temperature fluctuations, and physical damage. They typically have additional layers of insulation, protective jackets, and armor to enhance durability.
Indoor cables, on the other hand, are designed for use in controlled indoor environments where they are not exposed to outdoor elements. They may have simpler constructions with lighter insulation and jackets since they do not need to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
Outdoor cables are engineered to withstand exposure to moisture, sunlight, extreme temperatures, and other outdoor elements without degradation in performance. They are often water-resistant, UV-resistant, and designed to resist corrosion and damage from pests or rodents.
Indoor cables do not require the same level of protection against outdoor elements since they are typically installed in climate-controlled environments where exposure to moisture, sunlight, and temperature extremes is minimal.
Outdoor cables are designed for installation in outdoor environments, including aerial installations, direct burial in the ground, or installation in underground conduits. They are engineered to withstand the rigors of outdoor installation methods and may require additional protection such as armored jackets or water-blocking features.
Indoor cables are installed in indoor environments such as homes, offices, data centers, or industrial facilities. They are typically installed using standard indoor wiring methods and do not require the same level of protection as outdoor cables.
Outdoor cables may need to meet specific regulatory standards and certifications for outdoor use, such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) ratings for fire resistance and NEC (National Electrical Code) requirements for burial depths and conduit specifications.
Indoor cables may also need to meet regulatory standards, but these standards may differ from those required for outdoor cables since indoor cables are not subject to the same environmental hazards.
Outdoor cables are designed to withstand harsh outdoor conditions and are suitable for outdoor installations such as telecommunications networks, power distribution systems, and surveillance systems. Indoor cables, on the other hand, are designed for use in controlled indoor environments and do not require the same level of protection against outdoor elements. It’s essential to choose the appropriate type of cable based on the specific application and environmental conditions to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
In conclusion, outdoor cables play a critical role in enabling communication, power distribution, and data transmission across diverse outdoor environments. By understanding the various types, models, and applications of cables, along with key considerations for selection, organizations and individuals can make informed decisions to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and longevity of their installations. Whether it’s for telecommunications networks, power grids, or outdoor surveillance systems, the right outdoor cable can pave the way for seamless connectivity and efficient operations in the great outdoors.
When people hear the term mineral insulated cable, many immediately think of harsh environments like…
As telecommunication networks and power transmission systems grow rapidly, the demand for reliable and cost-effective…
In large-scale oil and gas projects, industrial cables are not just accessories—they are the "nervous…
In the world of electrical connections, cable lugs—also known as cable ears or cable terminals—are…
When choosing the right rubber cable for an electrical engineering project, it is critical to…
Dear partners and customers: January 29th, 2025 is the Chinese Lunar New Year – Spring…