As HV cable, it can be divided into aluminum high-voltage cables and copper high-voltage cables according to different materials. With the complex environmental conditions and special requirements in areas, the use of copper core cables is more reliable in terms of quality and safety. According to our construction, the selection of cable models should refer to the surrounding environment, the corresponding means of laying, and the performance of electrical equipment.
Types of VERI High Voltage Cable
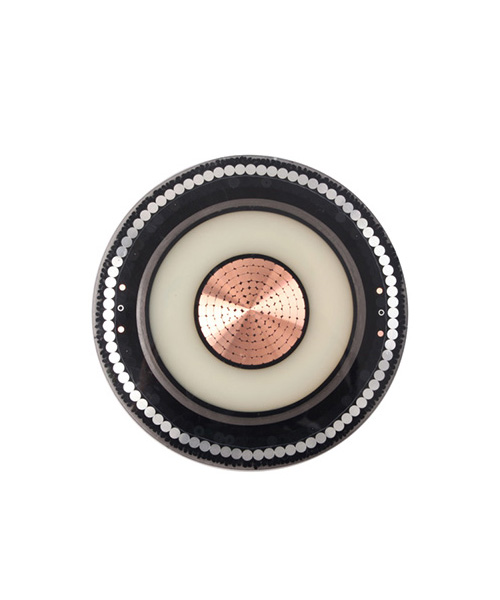
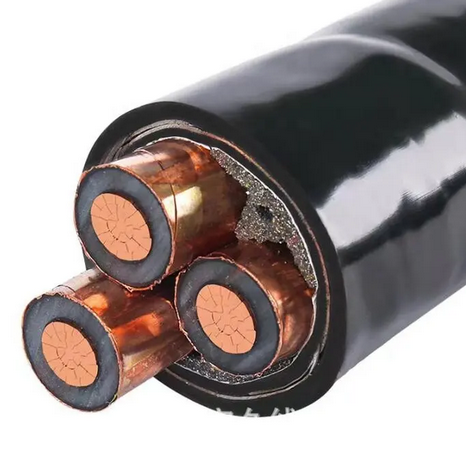
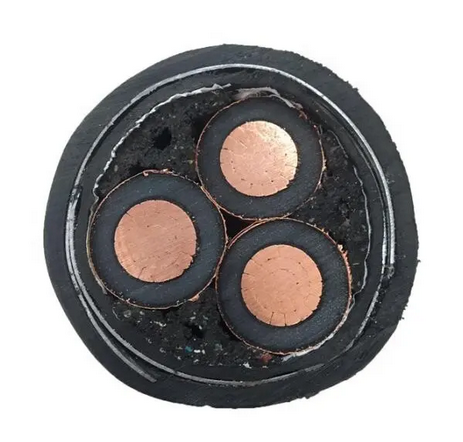
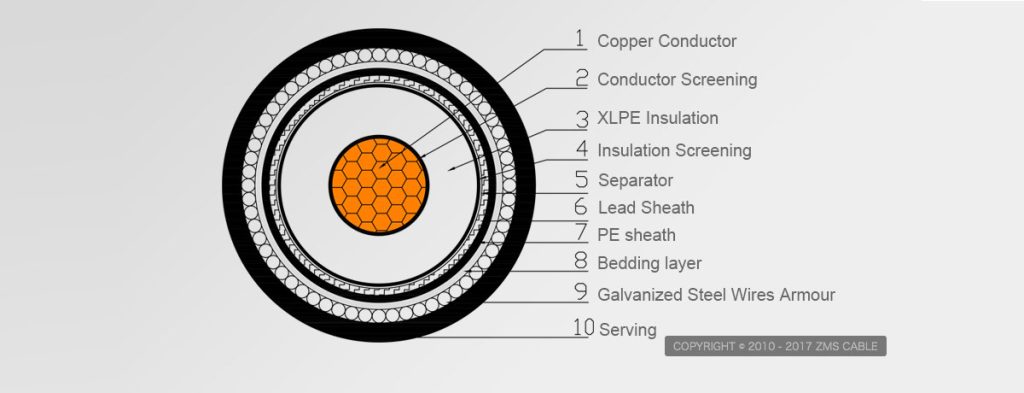
YJV22 3 Core HV Armored Steel Tape Copper Cable
Insulated PVC sheathed power cables are used for power transmission and distribution systems with rated voltages of 0.6/1kv, 1.8/3kv, 3.6/6kv, 6/10kv, 8.7/10kv, 8.7/15kv, 12/20kv, 21/35kv, 26/35kv.
1. XLPE insulated, PVC sheathed power cables (YJV, YJLV) are suitable for indoors, tunnels, pipes, and buried in soil (not subject to mechanical force)
2. XLPE insulated, steel tape armored PVC sheathed power cables (YJV22, YJLV22) are suitable for indoor, tunnel, pipe penetration, and buried in soil
3. XLPE insulated, steel wire armored PVC sheathed power cables (YJV32, 42, YJLV32, 42) are suitable for shafts, water, places with drop, and can withstand external forces.
The minimum bend radius of the cable
Item | Three -core | |
Unarmored | Armored | |
Minimum bend radius of the cable in course of installation. | 15D | 12D |
The minimum bend radius of the cable close to the junction box and terminal | 12D | 10D |
Note: D is outer diameter of the cable | ||
Size Information
Cross section area(mm²) | Insulated thickness(mm) | Metal shield thickness(mm) | Jacket thickness(mm) | OD(mm) | Weight(kg/km) |
3×25 | 4.5 | 30×0.10 | 2.4 | 44.8 | 2251.6 |
3×35 | 4.5 | 40×0.10 | 2.5 | 47.2 | 2655.9 |
3×50 | 4.5 | 40×0.10 | 2.6 | 50.4 | 3217.3 |
3×70 | 4.5 | 40×0.10 | 2.7 | 54.0 | 3957.2 |
3×95 | 4.5 | 40×0.10 | 2.8 | 57.7 | 4884.7 |
3×120 | 4.5 | 40×0.10 | 2.9 | 60.9 | 5754.2 |
3×150 | 4.5 | 40×0.10 | 3.0 | 64.5 | 6788.0 |
3×185 | 4.5 | 40×0.10 | 3.1 | 68.2 | 7961.6 |
3×240 | 4.5 | 40×0.10 | 3.3 | 73.5 | 9801.3 |
3×300 | 4.5 | 40×0.10 | 3.4 | 78.3 | 11725.3 |
3×400 | 4.5 | 40×0.10 | 3.7 | 85.8 | 14799.2 |
Product structure features:
1. Has good high-temperature resistance: XLPE insulation uses chemical or physical methods to change the structure of polyethylene molecules into a three-dimensional network structure. The three-dimensional network structure has good heat resistance and can be used in Long-term work at a high temperature of 90 ogo Celsius, the lifespan can be as long as 40 afọ.
2. It has good insulation performance: polyethylene not only retains the insulation performance of cross-linked polyethylene but also has a further improvement in insulation resistance.
3. High mechanical properties: hardness, stiffness, wear resistance, and impact resistance have been improved
4. Chemical resistance: XLPE itself has strong acid and alkali resistance and oil resistance
5. Environmental protection: Since the products of cross-linked polyethylene combustion are water and carbon dioxide, the environmental pollution is low, and it meets the fire safety requirements.
6. The maximum rated temperature of the cable conductor is 90°C, and the maximum temperature during the short circuit (the longest duration does not exceed 5S) does not exceed 250°C.
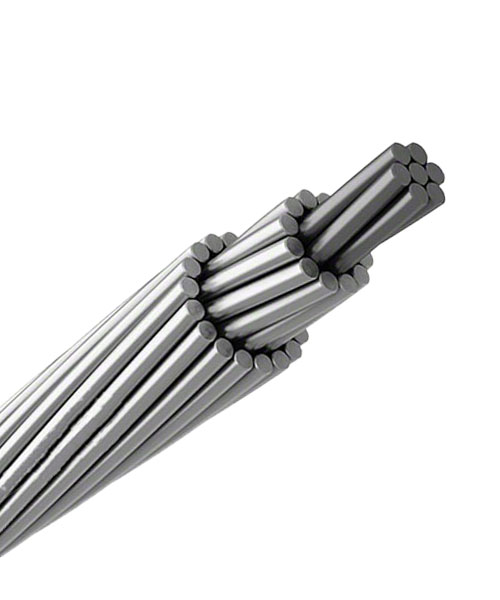
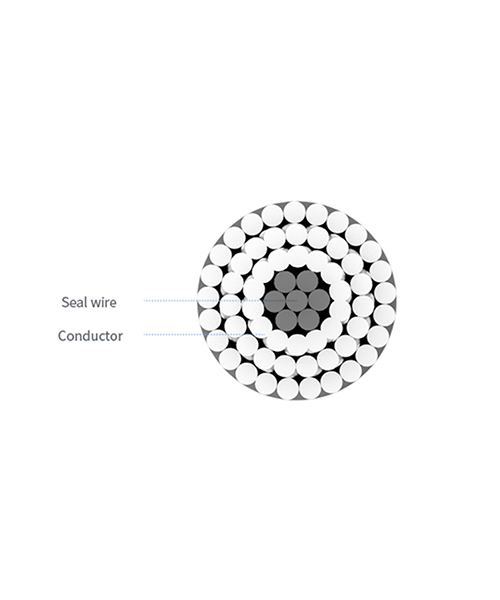
High Voltage Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced Cable
Aluminum conductor, steel reinforced overhead cable, is mainly used in power transmission lines with high voltage.
Its advantages include high mechanical strength, good electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, light unit volume, easy erection, high-temperature resistance, simple structure, convenient installation, good maintenance, na nnukwu nnyefe ikike. The High-voltage steel cable of ACSR consists of a solid or stranded steel core surrounded by strands of aluminum.
- Onye nduzi: Aluminum
- Street lighting conductor: Round-stood or compacted Aluminum conductor
- Mkpuchi: LDPE/HDPE/XLPE/PVC
Ọkọlọtọ&Ntụaka:GB/T12527/IEC60502/NFC 33-209/BS 7870/ANSI/ICEA S-76-474 AS/NZS 35601
HV ACSR Conductor According to GOST 839-80
| Section | Aluminum part | Steel part | Min. Breaking Strength | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of wires | Nom. wire diameter | Number of wires | Nom. wire diameter | |||
| 1 | 16/2.7 | 6 | 1.85 mm. | 1 | 1.85 mm. | 6,220 N. |
| 2 | 25/4.2 | 6 | 2.30 mm. | 1 | 2.30 mm. | 9,296 N. |
| 3 | 35/6.2 | 6 | 2.80 mm. | 1 | 2.80 mm. | 13,524 N. |
| 4 | 50/8.0 | 6 | 3.20 mm. | 1 | 3.20 mm. | 17,112 N. |
| 5 | 70/11 | 6 | 3.80 mm. | 1 | 3.80 mm. | 24,130 N. |
| 6 | 70/72 | 18 | 2,20 mm. | 19 | 2.20 mm. | 96,862 N. |
| 7 | 95/16 | 6 | 4.50 mm. | 1 | 4.50 mm. | 33,369 N. |
| 8 | 120/19 | 26 | 2.40 mm. | 7 | 1.85 mm. | 41,521 N. |
| 9 | 120/27 | 30 | 2.20 mm. | 7 | 2.20 mm. | 49,465 N. |
| 10 | 150/19 | 24 | 2.80 mm. | 7 | 1.85 mm. | 46,307 N. |
| 11 | 150/24 | 26 | 2.70 mm. | 7 | 2.10 mm. | 52,279 N. |
| 12 | 150/34 | 30 | 2.50 mm. | 7 | 2.50 mm. | 62,643 N. |
| 13 | 185/24 | 24 | 3.15 mm. | 7 | 2.10 mm. | 58,075 N. |
| 14 | 185/29 | 26 | 2.98 mm. | 7 | 2.30 mm. | 62,055 N. |
| 15 | 185/43 | 30 | 2.80 mm. | 7 | 2.80 mm. | 77,767 N. |
| 16 | 205/27.0 | 24 | 3.30 mm. | 7 | 2.20 mm. | 63,740 N. |
| 17 | 240/32 | 24 | 3.60 mm. | 7 | 2.40 mm. | 75,050 N. |
| 18 | 240/39 | 26 | 3.40 mm. | 7 | 2.65 mm. | 80,895 N. |
| 19 | 240/56 | 30 | 3.20 mm. | 7 | 3.20 mm. | 98,253 N. |
| 20 | 300/39 | 24 | 4.00 mm. | 7 | 2.65 mm. | 90,574 N. |
| 21 | 300/48 | 26 | 3.80 mm. | 7 | 2.95 mm. | 100,623 N. |
| 22 | 300/204 | 54 | 2.65 mm. | 37 | 2.65 mm. | 284,579 N. |
| 23 | 330/43.0 | 54 | 2.80 mm. | 7 | 2.80 mm. | 103,784 N. |
| 24 | 400/18 | 42 | 3.40 mm. | 7 | 1.85 mm. | 85,600 N. |
| 25 | 400/51 | 54 | 3.05 mm. | 7 | 3.05 mm. | 120,481 N. |
| 26 | 400/64 | 26 | 4.34 mm. | 7 | 3.40 mm. | 129,183 N. |
| 27 | 400/93 | 30 | 4.15 mm. | 19 | 2.50 mm. | 173,715 N. |
| 28 | 500/27 | 76 | 2.84 mm. | 7 | 2.20 mm. | 112,188 N. |
| 29 | 500/64 | 54 | 3.40 mm. | 7 | 3.40 mm. | 148,257 N. |
| 30 | 600/72 | 54 | 3.70 mm. | 19 | 2.20 mm. | 183,835 N. |
Ngwa
The type of these cables uses in electricity distribution lines laying across rivers and valleys where special geographical creatures exist. The conductor of ACSR represents the most important component of an overhead power line because they have to ensure economical and reliable transmission and contribute considerably to the total line costs.
Laying of VERI High Voltage Cables
Inspection before cable laying: whether the model and specifications meet the requirements, the insulation should be good, the appearance should be complete, and there should be no traces of trauma.
A spare length should be reserved near the cable terminal, and a spare length should be reserved for the directly buried cable in the wave-shaped laying.
The distance between each fulcrum of the cable shall be as specified in the design.
When there are no design regulations, it should not be greater than rubber cable and plastic cables are horizontal 1M, vertical 2M, and cables suspended on steel cables are horizontal 0.75M.
The bending radius of the cable should not be less than 10 ugboro mpụta dayameta nke eriri (armored or unarmored multicore plastic insulated power cable).
When laying the cables, the cables should be drawn out from the upper end of the reel, and avoid friction and drag of the cables on the bracket and the ground.
The cables should not be crossed when laying, they should be neatly arranged, fixed, and signs should be installed.
There should be firm stakes at the corners of the directly buried cables. When cables enter cable trenches, tunnels, buildings, and pipes, the entrances and exits should be closed.
Clamps and fixtures for AC single-core cables should not have a closed magnetic circuit composed of iron.
Ụgbọ njem na ọrụ ọkachamara

Veri Cable nwere ọtụtụ ụzọ iji chebe eriri gị, nwere nkwakọ mbupu siri ike na ọkachamara yana mkpuchi zuru oke. Tupu mbupu, anyi eriri a na-akwakọba n'ime osisi reels na corrugated igbe. N'oge njem, iji chebe eriri eriri site na mmiri mmiri, anyị na-eji BOPP teepu na-ejide onwe ya na-abụghị hygroscopic mechie ha.

Ọ bụrụ na enwere nsogbu dị mma dịka nkwakọ ngwaahịa mebiri emebi na mmebi elu ngwaahịa n'ebe ahụ mgbe a na-anata ngwongwo, ọ bụrụ na achọpụtara na ngwongwo ahụ bụ eziokwu, ngwa ahịa adabaghị n'usoro, na nsogbu dị mma nke onye ahịa chọtara n'oge ntinye, A kwadoro usoro ịtọgbọ na iji ya bụ nsogbu dị mma nke ngwaahịa ahụ n'onwe ya, Ọ bụrụ na nnyefe adịghị na nkwekọrịta chọrọ, Biko kpọtụrụ ụlọ ọrụ anyị ozugbo.