Drag chain cables, also known as cable carriers or energy chains, are specialized cables designed to withstand the rigorous demands of dynamic applications where cables are subjected to continuous movement. These cables are engineered to endure repetitive flexing, bending, and twisting, making them indispensable in various industrial and robotic applications. In this comprehensive guide, VERI cable will explore what drag chain cables are, how they function, and the best practices for using them to ensure optimal performance and longevity.

Specifically Understanding Drag Chain Cables
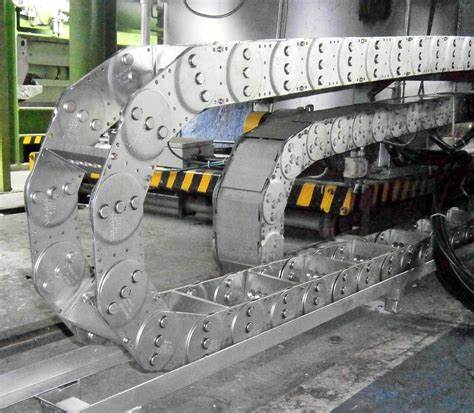
What Are Drag Chain Cables?
Drag chain cables are cables specifically designed to operate in environments where continuous movement is required. Unlike standard cables, drag chain cables can endure thousands or even millions of cycles of repetitive motion without suffering damage or degradation in performance. These cables are used in conjunction with drag chains, which are mechanical systems that guide and protect the cables, preventing tangling, excessive wear, and potential hazards in dynamic applications.
Key Characteristics of Drag Chain Cables
Drag chain cables possess several key characteristics that distinguish them from standard cables:
- High Flexibility: Drag chain cables are highly flexible, allowing them to bend and twist repeatedly without breaking or deteriorating.
- Onuno: These cables are constructed with durable materials that can withstand harsh industrial environments, including exposure to chemicals, oils, and extreme temperatures.
- Torsional Strength: Drag chain cables are designed to resist torsion (twisting) and can handle multidimensional movement.
- Resistance to Wear and Tear: The outer sheath of drag chain cables is typically made from abrasion-resistant materials to protect the internal conductors from damage.
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): Many drag chain cables are shielded to prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI) from affecting the signal integrity of the cables.
Applications of Drag Chain Cables
Drag chain cables are used in various industries where machinery and equipment require reliable and continuous movement. Some of the most common applications include:
- Robotics: Drag chain cables are essential in robotic arms and automated systems, where cables need to move freely without kinking or breaking.
- CNC Machines: In computer numerical control (CNC) machines, drag chain cables ensure the smooth and continuous operation of the machine’s moving parts.
- Material Handling: Conveyor systems and automated material handling equipment often utilize drag chain cables to ensure continuous operation without cable damage.
- Packaging Machines: In the packaging industry, where high-speed operations are common, drag chain cables help maintain the efficiency and safety of the machinery.
- Automotive Manufacturing: Drag chain cables are used in various stages of automotive manufacturing, particularly in assembly lines where machinery operates continuously.
- Medical Equipment: In medical devices that require precision and reliability, drag chain cables are used to ensure consistent performance.
More Types of Drag Chain Cables
Drag chain cables come in various types, each designed for specific applications and environments. Understanding the different types of drag chain cables can help you choose the right one for your needs.
1. Single-Core Drag Chain Cables
Single-core drag chain cables consist of a single conductor enclosed within an insulating material. These cables are typically used in applications where space is limited, and only a single electrical connection is required. They are often found in small robotic systems and compact machinery.
2. Multi-Core Drag Chain Cables
Multi-core drag chain cables contain multiple conductors, each insulated individually, and enclosed within a single outer sheath. These cables are ideal for applications requiring multiple electrical connections, such as in CNC machines and complex robotic systems.
3. Data and Signal Cables
Data and signal drag chain cables are designed to transmit low-voltage signals with high fidelity. These cables are often shielded to prevent EMI, making them suitable for applications where signal integrity is critical, such as in medical equipment and precision instruments.
4. Power Cables
Power drag chain cables are used to transmit high voltage and current to machinery and equipment. These cables are designed to handle heavy-duty applications and are often reinforced with additional layers of insulation and protection.
5. Hybrid Cables
Hybrid drag chain cables combine multiple types of conductors within a single cable. Ọmụmaatụ, a hybrid cable may include power, data, and signal conductors, making it a versatile solution for complex machinery and systems.
How to Choose the Right Drag Chain Cable
Selecting the right drag chain cable for your application involves considering several factors. The wrong choice can lead to premature cable failure, costly downtime, and safety hazards. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you choose the right drag chain cable.
1. Assess the Application Requirements
Start by assessing the specific requirements of your application. Consider factors such as the type of movement (bending, twisting, or both), the speed of operation, the length of travel, and the environmental conditions (temperature, iru mmiri, chemical exposure).
2. Determine the Type of Cable
Based on the application requirements, determine whether you need a single-core, multi-core, data, signal, power, or hybrid cable. Ọmụmaatụ, if you need to transmit high voltage, a power cable is the right choice, while a data cable is best for low-voltage signal transmission.
3. Consider the Flexibility and Bending Radius
Drag chain cables are available in different levels of flexibility. The bending radius is the minimum radius the cable can bend without damaging the internal conductors. Ensure that the cable you choose has a bending radius suitable for your application. If your application involves tight bends, select a cable with a smaller bending radius.
4. Check the Torsional Strength
Choose a drag chain cable with high torsional strength if your application involves twisting movements. This will ensure that the cable can handle the twisting motion without suffering from internal damage or conductor breakage.
5. Evaluate the Environmental Conditions
Consider the environmental conditions where the cable will be used. If the cable will be exposed to chemicals, oils, or extreme temperatures, choose a cable with a sheath material that can withstand these conditions. Additionally, if the cable will be used in outdoor applications, ensure it is UV-resistant.

6. Review the Manufacturer’s Specifications
Always review the manufacturer’s specifications and recommendations for the drag chain cable. This includes the maximum number of cycles the cable can handle, the temperature range, the bending radius, and any special features like shielding for EMI protection.
7. Consult with Experts
If you’re unsure which drag chain cable to choose, consult with experts or the cable manufacturer. They can provide valuable insights and recommendations based on your specific application needs.
Best Practices for Installing Drag Chain Cables
Proper installation of drag chain cables is crucial for ensuring their longevity and performance. Here are some best practices to follow when installing drag chain cables:
1. Use the Correct Drag Chain
Ensure that the drag chain (cable carrier) you use is compatible with the drag chain cable. The drag chain should provide adequate space for the cable to move freely without being compressed or restricted. Additionally, the drag chain should support the weight of the cable and any other components housed within it.
2. Follow the Recommended Bending Radius
During installation, make sure the cable is not bent beyond its recommended bending radius. Exceeding the bending radius can cause internal damage to the conductors, leading to premature cable failure.
3. Secure the Cable Properly
Secure the cable at both ends to prevent it from slipping or moving within the drag chain. Agbanyeghị, avoid clamping the cable too tightly, as this can cause damage to the insulation and internal conductors.
4. Avoid Overfilling the Drag Chain
Overfilling the drag chain with too many cables can restrict movement and cause excessive wear on the cables. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the maximum fill capacity of the drag chain.
5. Ensure Proper Cable Alignment
During installation, ensure that the cable is properly aligned within the drag chain. Misalignment can cause unnecessary stress on the cable and lead to premature wear and tear.
6. Perform Regular Inspections and Maintenance
Regularly inspect the drag chain cables for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Routine maintenance can help identify potential issues before they lead to cable failure, ensuring continuous and reliable operation.

Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Drag Chain Cables
Misusing drag chain cables can lead to various issues, including cable failure, machinery downtime, and safety hazards. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
1. Using Standard Cables Instead of Drag Chain Cables
One of the most common mistakes is using standard cables in applications that require drag chain cables. Standard cables are not designed to withstand continuous movement and will fail prematurely in such environments.
2. Ignoring the Bending Radius
Exceeding the recommended bending radius is a frequent cause of cable failure. Always ensure that the cable is installed with the proper bending radius to avoid internal conductor damage.
3. Overloading the Drag Chain
Overloading the drag chain with too many cables or using a drag chain that is too small for the application can lead to cable damage and restricted movement. Always use a drag chain that is appropriately sized for the cables it will carry.
4. Neglecting Environmental Factors
Failing to consider the environmental conditions where the cable will be used can lead to premature cable failure. Ensure that the cable’s sheath material is suitable for the environment, especially if the cable will be exposed to kemikal, oils, or extreme temperatures.
5. Improper Cable Securing
Improperly securing the cable at the ends or along the drag chain can cause the cable to move or shift, leading to wear and potential failure. Make sure the cable is secured properly without being too tight.
The Future of Drag Chain Cables
As industries continue to advance, the demand for more sophisticated and durable drag chain cables will increase. Innovations in materials, imewe, and manufacturing processes are expected to develop drag chain cables that can handle even more extreme conditions, higher speeds, and more complex movements. Additionally, the integration of smart technologies, such as sensors and monitoring systems, into drag chain cables could provide real-time data on cable performance, further enhancing their reliability and lifespan.
Drag chain cables play a critical role in ensuring the reliable operation of machinery and equipment in dynamic applications. By understanding what drag chain cables are, how they function, and the best practices for their use, you can ensure that your cables provide long-lasting performance and help minimize downtime and maintenance costs.
When choosing and installing drag chain cables, always consider the specific requirements of your application, including the type of movement, environmental conditions, and the bending radius. By following the guidelines and avoiding common mistakes, you can maximize the lifespan of your drag chain cables and ensure the smooth and efficient operation of your machinery.
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities of drag chain cables, offering even greater performance and reliability in the years to come. Whether you’re in robotics, mmepụta ihe, or any other industry that relies on dynamic motion, understanding and utilizing drag chain cables effectively is essential for maintaining a competitive edge.