Kejbils tar-ram ta 'vultaġġ għoli huma komponenti essenzjali fid-distribuzzjoni u t-trasmissjoni ta' enerġija elettrika, toffri kemm durabilità kif ukoll konduttività elettrika eċċellenti. Nifhmu l-istruttura, speċifikament in-numru ta 'qlub fi ħdan dawn il-kejbils, huwa kruċjali biex jiddeterminaw il-funzjonalità u l-applikazzjonijiet tagħhom f'diversi industriji. Dan l-artikolu jesplora kemm qlub kejbil tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli normalment għandu u jidħol fl-applikazzjonijiet tipiċi ta 'dawn il-kejbils f'setturi differenti.

X'inhu kejbil tar-ram ta 'vultaġġ għoli?
Qabel ma tgħaddas fin-numru ta 'qlub, Huwa importanti li tiċċara dak li jikkostitwixxi kejbil tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli. Dawn il-kejbils huma ddisinjati speċifikament biex jittrasmettu l-enerġija elettrika f'vultaġġi għoljin, ġeneralment bejn 1 KV u 33 kV, Għalkemm xi kejbils ta 'vultaġġ għoli jistgħu jġorru vultaġġi ferm ogħla, partikolarment fin-netwerks ta 'trasmissjoni. Il-qalba tal-kejbil hija magħmula mir-ram, magħruf għall-konduttività elettrika superjuri tiegħu meta mqabbel ma 'materjali oħra, tagħmilha għażla popolari f'sistemi ta 'vultaġġ għoli.
Ir-rwol primarju ta 'kejbil tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli huwa li tiżgura trasmissjoni ta' enerġija effiċjenti filwaqt li timminimizza t-telf ta 'enerġija u ż-żamma tas-sigurtà. Dawn il-kejbils huma tipikament iżolati b'materjali robusti biex jifilħu kundizzjonijiet ambjentali ħorox u stress elettriku.
Kemm qlub għandu kejbil tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli normalment?
Kejbils tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli b'qalba waħda
Wieħed mill-aktar Tipi komuni ta 'kejbils tar-ram ta' vultaġġ għoli huwa l-kejbil tal-qalba waħda. Kif jissuġġerixxi l-isem, Kejbil tal-qalba waħda fih konduttur wieħed biss (qalba) imdawwar minn insulazzjoni u saffi protettivi. Dawn il-kejbils jintużaw ħafna f'diversi applikazzjonijiet ta 'vultaġġ għoli, Speċjalment f'sistemi ta 'trasmissjoni ta' enerġija fuq skala kbira.
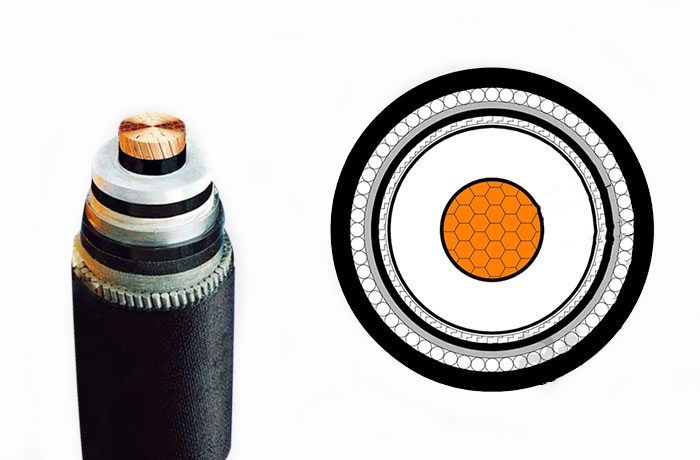

Applikazzjonijiet ta 'kejbils tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli ta' qalba waħda:
- Linji ta 'trasmissjoni ta' enerġija: Kejbils tar-ram b'qalba waħda jintużaw biex jittrasmettu qawwa ta 'vultaġġ għoli fuq distanzi twal, partikolarment bejn is-substations u konsumaturi kbar tal-enerġija bħall-impjanti industrijali.
- Sistemi ta' Enerġija Rinnovabbli: Huma wkoll użati ħafna fl-irziezet solari u tar-riħ, fejn jgħinu biex jittrasmettu l-enerġija minn sorsi ta 'enerġija rinnovabbli għall-grilja.
- Substations: Kejbils ta 'qalba waħda huma preferuti f'substazzjonijiet minħabba l-faċilità ta' installazzjoni tagħhom u l-abbiltà li jimmaniġġjaw tagħbijiet ta 'kurrent għoli.
Kejbils tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli b'ħafna qalba
B'kuntrast ma 'kejbils ta' qalba waħda, kejbils tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli b'ħafna qalba fih kondutturi multipli fi ħdan għant wieħed. In-numru ta 'qlub f'dawn il-kejbils jista' jvarja, tipikament tvarja minn 2 biex 4, Għalkemm applikazzjonijiet speċifiċi jistgħu jeħtieġu kejbils b'aktar qlub. Kejbils multi-core huma spiss preferuti f'ambjenti fejn l-ispazju huwa limitat, Peress li jistgħu jittrasmettu ċirkwiti elettriċi multipli fl-istess ħin mingħajr il-ħtieġa għal kejbils separati.
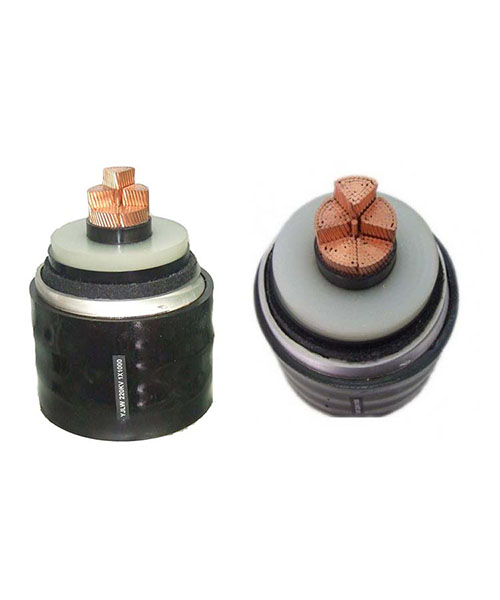

Kejbils tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli b'żewġ qalba
Kejbils b'żewġ qalba huma inqas komuni f'applikazzjonijiet ta 'vultaġġ għoli meta mqabbla ma' tipi ta 'qalba waħda. Madankollu, Xi drabi jintużaw f'ambjenti industrijali speċjalizzati fejn kemm is-sinjali tal-enerġija kif ukoll tal-komunikazzjoni għandhom jiġu trasmessi fuq l-istess kejbil.
Kejbils tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli bi tliet qalba
Kejbils tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli bi tliet qalba huma aktar prevalenti f'applikazzjonijiet ta 'vultaġġ medju sa għoli. It-tliet qlub jirrappreżentaw trasmissjoni ta 'enerġija bi tliet fażijiet, li huwa essenzjali għal ħafna sistemi industrijali u distribuzzjoni ta 'enerġija fuq skala kbira.
Applikazzjonijiet ta 'kejbils tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli bi tliet qalba:
- Sistemi ta 'enerġija industrijali: Dawn il-kejbils jintużaw ħafna f'industriji fejn l-enerġija bi tliet fażijiet hija essenzjali biex issuq muturi kbar u makkinarju.
- Netwerks ta 'distribuzzjoni ta' l-enerġija: Fid-distribuzzjoni tal-enerġija lokali u reġjonali, Kejbils bi tliet qalba jiżguraw fluss ta 'enerġija effiċjenti għal residenzjali, kummerċjali, u klijenti industrijali.
- Applikazzjonijiet tal-Baħar u Offshore: F'ambjenti fejn l-ispazju huwa limitat, bħal riggijiet u vapuri taż-żejt barra mill-kosta, Kejbils tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli bi tliet qalbi spiss jintużaw għad-distribuzzjoni tal-enerġija.
Kejbils tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli b'erba 'qalba
Kejbils b'erba 'qalba ġeneralment jintużaw f'applikazzjonijiet ta' vultaġġ baxx sa medju, Għalkemm varjanti ta 'vultaġġ għoli jeżistu għal bżonnijiet speċifiċi. F'xenarji ta 'vultaġġ għoli, Ir-raba 'qalba tista' taġixxi bħala newtrali jew bħala konduttur tad-dinja, Jiddependi fuq il-konfigurazzjoni tas-sistema.
Applikazzjonijiet ta 'kejbils tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli b'erba' qalba:
- Sistemi ta 'kostruzzjoni u bini: Dawn il-kejbils spiss jintużaw fi proġetti ta 'kostruzzjoni għad-distribuzzjoni tal-enerġija fin-netwerks tal-bini.
- Distribuzzjoni tal-enerġija taħt l-art: Meta l-enerġija teħtieġ li tiġi trasmessa taħt l-art, Kejbils tar-ram b'erba 'qalba huma komunement użati biex jipprovdu stabbiltà u sensja f'każ ta' falliment ewlieni.
Fatturi li jinfluwenzaw in-numru ta 'qlub fil-kejbils tar-ram ta' vultaġġ għoli
Diversi fatturi jinfluwenzaw in-numru ta 'qlub magħżula għal kejbil tar-ram ta' vultaġġ għoli:
- Applikazzjoni: Ir-rekwiżiti speċifiċi tal-applikazzjoni, bħal jekk tintużax għat-trasmissjoni tal-enerġija, distribuzzjoni, jew operazzjonijiet industrijali, Se jiddetta n-numru ta 'qlub.
- Tip ta 'kurrent (AC jew DC): Kurrent alternattiv (AC) Sistemi tipikament jużaw kejbils bi tliet qalba biex jakkomodaw it-tliet fażijiet, Filwaqt li l-kurrent dirett (DC) Sistemi spiss jużaw kejbils ta 'qalba waħda jew b'żewġ qalba.
- Ambjent ta 'Installazzjoni: Il-post fejn se jkun installat il-kejbil - kemm jekk taħt l-art, overhead, jew fi bini - jista 'jinfluwenza wkoll l-għażla tal-konfigurazzjoni tal-qalba.
- Flessibilità tal-kejbil: Kejbils multi-core joffru flessibilità akbar f'installazzjonijiet fejn huma meħtieġa ċirkwiti multipli fl-istess spazju.
Applikazzjonijiet ewlenin ta 'kejbils tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli
1. Trasmissjoni u distribuzzjoni tal-enerġija
Kejbils tar-ram ta 'vultaġġ għoli jintużaw ħafna għal trasmissjoni tal-elettriku minn stazzjonijiet tal-ġenerazzjoni tal-enerġija għal substations u fl-aħħar mill-aħħar għall-utenti finali. Huma għandhom rwol vitali fl-iżgurar tat-trasferiment effiċjenti ta 'ammonti kbar ta' elettriku fuq distanzi twal, timminimizza t-telf ta 'enerġija.
2. Applikazzjonijiet industrijali
F'kumplessi industrijali kbar, Kejbils tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli jintużaw biex ifornu l-enerġija lil makkinarju tqil, muturi, u tagħmir ieħor li jeħtieġ tagħbijiet elettriċi sostanzjali. Id-disinn robust u l-konduttività għolja tar-ram jiżguraw li dawn is-sistemi jimxu sewwa mingħajr interruzzjonijiet.
3. Sistemi ta' Enerġija Rinnovabbli
Sistemi ta 'enerġija rinnovabbli, bħal irziezet tar-riħ u impjanti tal-enerġija solari, jiddependu fuq kejbils tar-ram ta 'vultaġġ għoli biex jgħaqqdu unitajiet ta' ġenerazzjoni mal-grilja ewlenija. Dawn il-kejbils huma essenzjali fit-trasport ta 'enerġija nadifa fuq distanzi twal, L-iżgurar li tilħaq il-grilja b'telf minimu.
4. Sistemi ta 'enerġija taħt l-art u sottomarini
Kejbils tar-ram ta 'vultaġġ għoli huma spiss installati taħt l-art jew taħt l-ilma biex jittrasmettu l-elettriku f'ambjenti fejn il-kejbils ta' l-għoli ma jkunux prattiċi. Dawn il-kejbils għandhom ikunu durabbli biżżejjed biex jifilħu kundizzjonijiet ħorox, inkluża l-umdità, pressjoni, u varjazzjonijiet fit-temperatura.
5. Sistemi ta 'Ferroviji u Trasport
L-industrija tat-trasport, speċjalment ferroviji, Użi wkoll Kejbils tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli għas-sinjalazzjoni, Sistemi ta 'kontroll, u linji tal-ferrovija elettrifikati. Dawn il-kejbils jipprovdu enerġija għat-tħaddim bla xkiel ta 'ferroviji elettriċi, trammijiet, u sistemi oħra tal-ferrovija b'veloċità għolja.

6. Infrastruttura tat-telekomunikazzjoni
Fit-telekomunikazzjonijiet, Kejbils tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli jintużaw flimkien ma 'mezzi oħra ta' trasmissjoni għal stazzjonijiet bażi ta 'enerġija, Ċentri tad-dejta, u infrastruttura ta 'komunikazzjoni oħra. Il-konduttività u l-affidabbiltà eċċellenti tar-ram jagħmluha għażla ideali għal dawn is-sistemi kritiċi.
Vantaġġi ta 'kejbils tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli
- Konduttività superjuri: Ir-ram għandu wieħed mill - L-ogħla konduttivitajiet elettriċi fost il-metalli, tagħmilha effiċjenti ħafna għat-trasmissjoni tal-enerġija b'telf minimu.
- Durabilità: Kejbils tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli huma ddisinjati biex jifilħu kundizzjonijiet ambjentali ħorox, inklużi temperaturi estremi, umdità, u stress mekkaniku.
- Reżistenza għall-korrużjoni: Ir-ram huwa naturalment reżistenti għall-korrużjoni, li huwa essenzjali għall-affidabbiltà fit-tul f'installazzjonijiet taħt l-art u taħt l-ilma.
- Flessibilità: Il-flessibilità tar-ram tippermetti installazzjoni aktar faċli fi spazji stretti u mogħdijiet ta 'rotta kumplessi, speċjalment f'konfigurazzjonijiet multi-core.
Kejbils tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli jiġu f'diversi konfigurazzjonijiet tal-qalba, Jiddependi fuq l-applikazzjoni speċifika u r-rekwiżiti tas-sistema elettrika. Qalba waħda, żewġ qalba, tliet qalba, u kejbils tar-ram b'erba 'qalba kollha għandhom l-użi tagħhom f'setturi differenti, li jvarjaw minn trasmissjoni ta 'enerġija u applikazzjonijiet industrijali għal enerġija rinnovabbli u telekomunikazzjonijiet. Il-versatilità tagħhom, flimkien mal-konduttività superjuri tar-ram, Durabilità, u affidabilità, jiżgura li kejbils tar-ram b'vultaġġ għoli jibqgħu komponent fundamentali fl-infrastruttura elettrika moderna.
Kemm jekk jintużaw fi grilji kbar tal-qawwa, Kumplessi industrijali, jew proġetti ta 'enerġija rinnovabbli, Dawn il-kejbils għandhom rwol kruċjali fl-iżgurar tat-trasmissjoni effiċjenti u sikura ta 'enerġija elettrika madwar id-dinja. Li tifhem il-konfigurazzjonijiet u l-applikazzjonijiet differenti tgħin lill-inġiniera u l-elettriċisti jagħżlu t-tip it-tajjeb ta 'kejbil għall-bżonnijiet speċifiċi tagħhom, L-iżgurar ta 'prestazzjoni u sigurtà ottimali.